Thousands of doctors and scientists are chasing solutions to the COVID-19 pandemic—from developing vaccines to the use of potent steroids as a frantic measure to save lives. One major insight finds obesity is a serious factor in both infections and consequential health problems. According to a recent CDC study, obesity may triple the risk of hospitalization, while approximately 78% of people who have been hospitalized, needed a ventilator, or died from COVID-19 have been overweight or obese.(1)
Stuart Long, CEO of InfoBionic, says that one of the most productive solutions for patients at risk is remote monitoring. “The comorbidities that put people at risk include conditions like diabetes and lung disease, but obesity has clearly emerged as a catalyst for some of COVID-19’s worst outcomes. If we want to help hospitals and doctors while still providing the best care for patients, any patient in this category might benefit from remote patient monitoring solutions in their homes.”
It’s a complex but unfortunately common problem, as an estimated 40% of American adults are obese.(2) The underlying pathologies of obesity only compound the virus’ effects. Fat in the abdomen pushes on the diaphragm, which restricts airflow in the lungs and compresses the chest cavity.(3) Furthermore, people with obesity tend to suffer from chronic, low-grade inflammation. Fat cells secrete several inflammation-triggering chemical agents called cytokines, which COVID-19 turns into a “cytokine storm,” flooding the body with agents that can kill tissue and damage organs.(4) Add the risk of severe blood clots and reduced immune cells, and it’s a recipe for disaster.
The most immediate public health goal, known as “flattening the curve,” was to ensure hospitals and medical staff aren’t overwhelmed by an influx of patients who require severe interventions. To this end, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a plan known as “Hospitals Without Walls,” designed to enable monitoring and treatment outside of those facilities.(5) A key element is remote cardiac monitoring, which embraces the automatic transmission of health data wirelessly. Patients used to clumsy cardiac harnesses may be surprised by how advanced remote patient monitoring (RPM) has become. RPM has an added benefit: by monitoring cardiac function, a physician can determine if an episode may require a hospital visit. This way, the nation’s overwhelmed hospital system is not further taxed with unnecessary visits. This also helps the patient monetarily, emotionally as it alleviates stress and avoids unneeded absences from work—which in turn, helps the economy and keeps the workforce going.
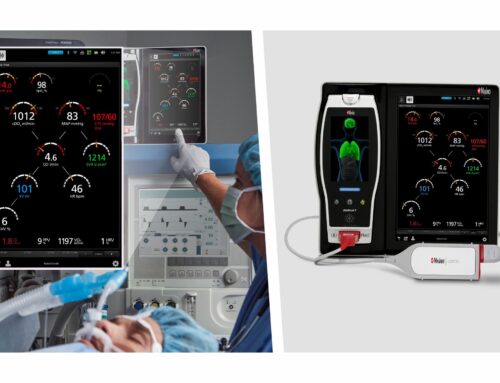
Devices like InfoBionic’s MoMe® Kardia cardiac monitor offers a hybrid solution for doctor-patient contact in regard to heart issues. Patients who have had COVID-19 or are experiencing significant after-effects can be equipped with a small monitor that connects via cellular connection to the cloud, resulting in reports and alerts to their cardiologist based on the recording of every single heartbeat and anomaly.
“When we look at the math, it becomes clear that remote patient monitoring can play a significant role in improving the health outcomes of obese patients who have either contracted COVID-19 or carry a better-than-average chance of catching it due to their comorbidities,” says Long. “Telehealth is all about care management and the road to better health outcomes starts with clean and accurate data, delivered via technology that is a whole lot safer for patients who are already at risk.”
About InfoBionic
InfoBionic is a digital health company transforming the efficiency and economics of ambulatory remote patient monitoring processes by optimizing clinical and real-world utility for the users that need it most – physicians and their patients. The Massachusetts-based team of seasoned entrepreneurs have had successful careers in healthcare, IT, medical devices and mobile technology, and bring specific expertise in remote monitoring and cardiology. They have seen first-hand the complexities of traditional cardiac arrhythmia detection and monitoring processes and designed the transformative MoMe® Kardia platform to remove the roadblocks hindering faster, more effective diagnosis and decision-making. Frost & Sullivan bestowed the 2019 North American Remote Cardiac Monitoring Technology Leadership Award upon InfoBionic. Visit www.infobionic.com.
- Center for Disease Control. “Obesity, Race/Ethnicity, and COVID-19 cdc.gov/obesity/data/obesity-and-covid-19.html Accessed April 2021
- Center for Disease Control. “Adult Obesity Facts” cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html Accessed April 2021
- Mafort TT, Rufino R, Costa CH, Lopes AJ. Obesity: systemic and pulmonary complications, biochemical abnormalities, and impairment of lung function. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2016;11:28. Published 2016 Jul 12. doi:10.1186/s40248-016-0066-z 4. Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry. “Connecting the Dots on Recent ECG Monitoring M&A Spree” mddionline.com/digital-health/connecting-dots-recent-ecg-monitoring-ma-spree Accessed March 2021
- New England Journal of Medicine. “Cytokine Storm” nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra2026131 Accessed April 2021
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. “CMS Announces Comprehensive Strategy to Enhance Hospital Capacity Amid COVID-19 Surge” cms.gov/newsroom/press-releases/cms-announces-comprehensive-strategy-enhance-hospital-capacity-amid-covid-19-surge Accessed April 2021